Contents
- Package definition
- Package structure
- Package internal information
- Merge Module
- Files
- Registries
- INI Files
- Shortcuts
- Fonts
- Services
- ODBC (Open DataBase Connectivity)
- System variables
- Properties
- Running custom code from the package
- Custom Actions
- System Search
- Upgrades
- Patching
- Upgrading
- De-hardcoding and Variabilization
- De-hardcoding
- Variabilization
- Vendor MSI
- Definition
- Seller Vendor Customization
- Direct vendor MSI
- Vendor MSI hidden in setup
- Vendor MSI with patch
- Modify an MSI vendor, from cab outside to cab inside, etc.
- Msiexec.exe commands
- Installing a package
- Repairing a package
- Uninstalling a package
- Administrative Installation
- Creating logs
- Applying a patch over a MSI
- Installation with MST
- Active-Setup Mechanism

ODBC (Open DataBase Connectivity)
As its name implies, an ODBC (Open DataBase Connectivity) connects your application to a variety of database management systems. Essentially, it allows applications to access a database (such as Access databases, dBase or Excel, etc.).
Classification of ODBC
- UserDSN: is a “data source” that is specific to a particular user; it is saved on the machine but is only available to the user who created it.
UserDSN ODBCs are registered in the user-specific registry:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\ODBC\ODBC.INI\Odbc Data sources
- SystemDSN: unlike UserDSN, it is saved locally but is not specific to a user.
Using a SystemDSN, any user who connects to a computer is allowed to access the data source.
SystemDSN ODBCs are registered in the machine-specific registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBC.INI\Odbc Data sources
- Drivers are libraries that implement functions for ODBC API; each driver is specific to a database management system.
Drivers practically play the role of a “translator” between an application and a database. The main utility of these drivers is that they allow us to interact with the databases, without the need to have a client program (provided by the database manufacturer).
ODBCs are managed through the ODBC Data Source Administrator, which is accessed from the Control Panel\Administrative Tools\Data Sources (ODBC).
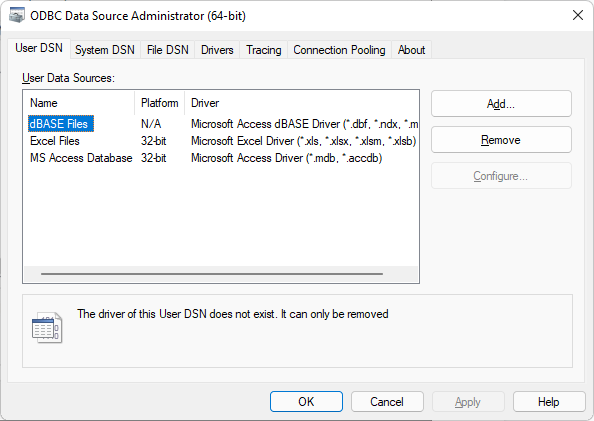
As specified above, ODBC information is stored in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBC.INI
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBCINST.INI
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\ODBC\ODBC.INI
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\ODBC\ODBCINST.INI,
Keys with ODBCINST.INI contain information about the drivers installed on the machine, and those with ODBC.INI contain information about the DSN on the machine.
You can also access information about ODBCs in the INI, ODBC.INI, and ODBCINST.INI files present in C:\WINDOWS.
ODBC specific tables
ODBCDataSource
This table contains the data sources related to the application.

ODBCDataSource Columns:
DataSource - input identifier
Component - foreign key in the Component table
Description - description of the source data
DriverDescription - the driver associated with the data source
Registration - how the data source is registered:
0 = per machine
1 = per user
ODBCSourceAttribute
This table contains information about the data attributes of the sources.
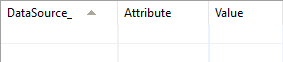
DataSource - datasource identifier, the primary key for the table
Attributes - attribute of the source data, the primary key for the table
Value - the value of the attribute
The ODBCDataSource and ODBCSourceAttribute tables install the DSN on the machine with all its information (both of these tables must be populated for a DSN to be installed).
The changes made by these two tables can be found in the
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBC.INI\DSName.
Note: A DSN from the corresponding tables can be placed even if the driver associated with the DSN is not in the package.
ODBCDriver
This table contains the ODBC drivers that belong to the application.

Driver - the driver identifier, the primary key for the table
Component - the foreign key in the component table
Description - the driver description
File - the dll file that generates the driver, foreign key in the File table
File_Setup - a driver-specific dll setup file, foreign key in the File table
ODBCAttribute
This table contains information about the attributes of drivers and translators.
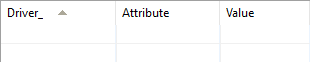
Driver - the driver identifier, primary key for this table, foreign key in the table
Attributes - the attribute name, the primary key for the table
Value - the value of the attribute
The changes that these two tables make on the machine are the following:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBCINST.INI\Driver_name - the entry written from the ODBCAttribute table, that contains all the driver description registry.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBCINST.INI\ODBC Drivers - where a string-type registry is created with the name of the driver and the value Installed.
- The C:\Windows\ODBCINST.INI file is altered with the extra driver.
To check a driver (if it is installed correctly), you can go to the Control Panel\Administrative Tools\Data Source (ODBC).
For further testing, you can add a DSN (user or system) by choosing the respective driver to set the DSN.
Note: An ODBCDriver cannot be set from the corresponding tables unless the required files (DriverDll and SetupDll) are in the package.
ODBCTranslator
This table contains ODBC translators that belong to the application.

Translator - the name of the translator, the primary key for the table
Component - the foreign key in the component table
Description - the description of the translator
File - the dll file, the foreign key in the File table
File_Setup - the dll setup file, the foreign key in the File table
The ODBCTranslator table writes in the following registry:
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBCINST.INI
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBCINST.INI\ODBC Translators
You can find a translator in the DSN (Administrative Tools\Data Sources) dialog where you want to load the translator. The display mode of a translator differs depending on the driver.
Easily manage your ODBC connections with Advanced Installer by using the ODBC Page.