Contents
- Package definition
- Package structure
- Package internal information
- Merge Module
- Files
- Registries
- INI Files
- Shortcuts
- Fonts
- Services
- ODBC (Open DataBase Connectivity)
- System variables
- Properties
- Running custom code from the package
- Custom Actions
- System Search
- Upgrades
- Patching
- Upgrading
- De-hardcoding and Variabilization
- De-hardcoding
- Variabilization
- Vendor MSI
- Definition
- Seller Vendor Customization
- Direct vendor MSI
- Vendor MSI hidden in setup
- Vendor MSI with patch
- Modify an MSI vendor, from cab outside to cab inside, etc.
- Msiexec.exe commands
- Installing a package
- Repairing a package
- Uninstalling a package
- Administrative Installation
- Creating logs
- Applying a patch over a MSI
- Installation with MST
- Active-Setup Mechanism

Services
Services are programs that run individually in the background. This can be said of many programs, such as anti-viruses. The difference is that the services load and run regardless of whether someone logs into the system or not, unlike a program launched from the StartUp folder.
You can view Services using the MS Configuration Utility and running the msconfig.exe executable.
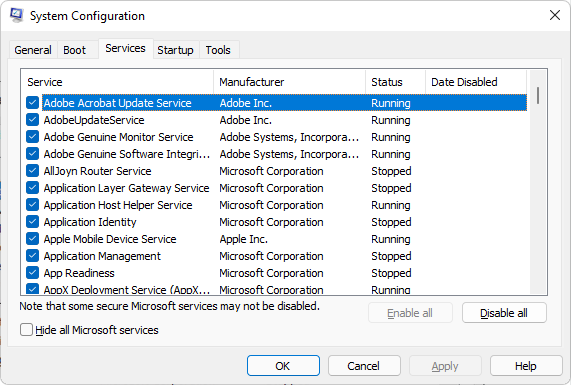
It offers rather limited information, in the sense that you can only see which services are turned on and which are not.
Another way to view the service is through services.msc, equivalent to the Control Panel\Administrative Tools\Services.

This method provides much more information about services, such as name, short description, status, etc.

Microsoft has assigned a display name for each service. It is the name that appears in the name column of the Windows Services window.
Attributes:
Service Name: The name of the service
Process Name/Path to execute: The name of the process that runs when the service is enabled.
Dependencies: The list of additional services that are required when the service is running.
These services are found “physically” in the machine registry: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services.
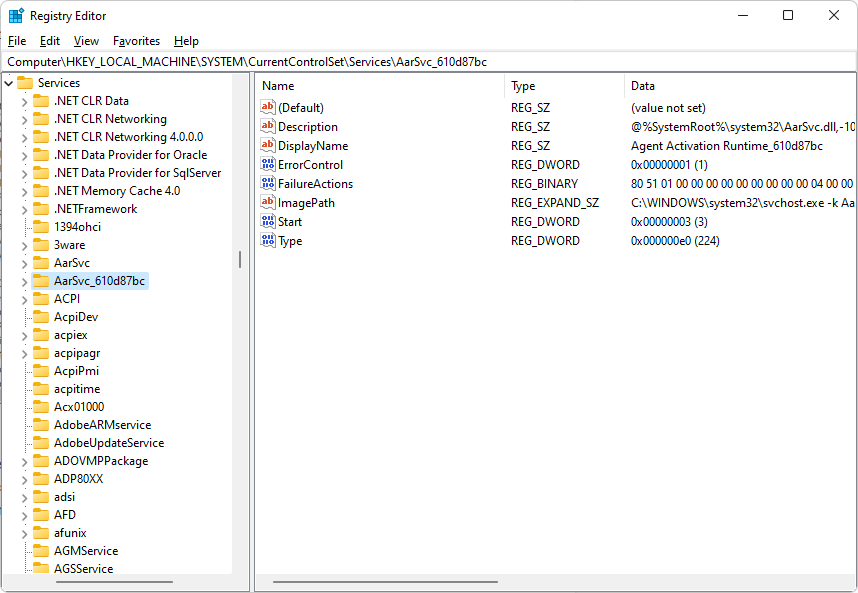
Classification of services
- automatic (start with the operating system)
- manuals (are started by applications/users)
Service status:
- Start
- Stop
- Disable
Services-specific tables
ServiceInstall
This table is used to install services:
ServiceInstall | Name | DisplayName | ServiceType | StartType | ErrorControl | LoadOrderGroup | Dependencies | StartName | Password | Arguments | Component | Description |
ServiceInstall Columns:
Name
- the name of the service, internal to windows
- must have a maximum of 256 characters
Display
- the name that appears to the user
- maximum 256 characters
ServiceInstall - primary key for this table
ServiceType
- the type of service
- accepted values:
0x00000010 - Win32 service, running its own process
0x00000020 - Win32 service, which streamlines a process
0x00000100 - Win32 service, which interacts with the desktop
StartType
- this column specifies when the process starts
- These are the accepted values:
2 - the service starts with the system (automatic)
3 - the service starts on request (manual)
4 - specify a service that cannot be started (disable)
ErrorControl
- this column specifies the action that Windows Installer must take if the service fails
to start
- accepted values:
0x00000000 - creates an error log and continues with the service start operation
0x00000001 - creates an error log, displays a message, and continues with the service start operation
0x00000003 - creates an error log (if possible) and restarts the system
LoadOrderGroup
- this column contains the order in which services will be started within a service group (if our service is also part of it)
- when left empty, it means that our service is not part of any group
Dependencies
- a list of services that must be started before starting the service from this entry
- services are separated by [~]
StartName
- the service starts with the name specified in this column
- if it has no value then the service uses the LocalSystem account to run
Password - the password of the account with which the service runs
Arguments - this column contains any arguments needed by the service to run
Component
- a foreign key in the Component table
- to create the service attached to this component, it must have the executable that is the basis of the service as key
Description - a description of the service being created
Virtually all the values populated by these columns correspond to the values in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Service_Name
From this table, you can install certain types of drivers, including Non-Plug & Play. These drivers are entered in the table similar to the services, except that in the column for the type of service (ServiceType column) other values are entered as follows:
0x00000001 - driver service
0x00000002 - file system driver service
The startup type of the driver also differs from the services. Non-plug & play drivers have 4 boot modes: Automatic, Boot, Demand, System. These startup types can be set from the table as for services in the StartType column as follows:
- Automatic - set the value to 2
- Boot - value 0
- Demand - value 3
- System - value 1
If you want the driver to be set as disabled, then add the value 0 in the StartType column.
On the machine, you can check the functionality of this type of driver from the DeviceManager to Non-Plug & Play Drivers (to see Non-Plug & Play Drivers, you must first access the View\Show hidden devices menu).
Attention: With the help of this table, the service/driver is installed but it does not start. That is why it is mandatory to use it along with the ServiceControl table.
For automatic services, you must perform an installation control service (start only for automatic ones) and a service control for uninstallation (stop and delete, both for automatic and manual ones).
ServiceControl
This table is used to control the installation and uninstallation of services.
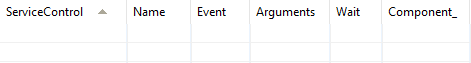
ServiceControl Columns:
ServiceControl - the primary key of this table
Name - the name of the service to be controlled
Event
- the operation to be performed on the service
- when a service is stopped, all services that depend on it are also stopped
- when a service is deleted, Windows Installer stops it
- values accepted at installation only:
1 - the service starts
2 - the service stops
8 - the service is deleted
- values accepted only when uninstalling:
16 - the service starts
32 - the service stops
128 - the service is deleted
Arguments
- a list of arguments for starting services
- arguments are separated by the reserved character [~]
Wait
- tells the system to “wait” before an actionLeaving this field blank or entering the value 1 tells Windows Installer to wait a maximum of 30 seconds for the service to follow an action
- it can be used when you want to allow additional time for critical events to return an error code
- the value 0 means that Windows Installer waits until SCM (Service Control Manager) reports that the service is in a standby state
Component - foreign key in the Component table
Note: With the Name column, you can start, stop, or delete services not created by our package.
With Advanced Installer you can easily install, control and configure Windows native services from the Services Page. More information about configuring services using Advanced Installer can also be found here, and in the service control properties.