MSI File - What is, how to open and edit it?
Introduction
We use MSI or EXE files whenever we install a Windows application, so we're pretty used to them. But, what is an MSI file, and what makes it different from an EXE file? What’s the easiest way to open and edit an MSI installer?
We’ll be answering this question, focusing on the following topics:
- What is an MSI file?
- How does installation work with the MSI format?
- How to open and edit an MSI file?
- What are the differences between MSI and EXE files?
- Are the MSI files safe?
What is an MSI file? What does MSI stand for?

The .MSI file extension stands for Microsoft Software Installer. It is a Windows Installer format that uses Microsoft's Windows Installer service to configure installer packages, such as Windows applications or update packages.
The MSI file extension is used to install software on Windows operating systems. It can be used to install, uninstall, configure, and update programs on the computer.
Vendors can offer their software packages in both .msi and .exe format, and you will most likely see both options on software download pages.
Learn why it's essential to understand the MSI package's components, how they work together, and how to use them in different processes across application packaging.
Check out the comprehensive MSI Packaging Training that includes: The Ebook and The Training Video Series. All FREE of charge!
How does installation work with the MSI format?

When you execute an MSI file format, the installation wizard will start. During this process, what generally happens is:
- Files are copied to the system,
- The registry keys get applied,
- Installation instructions, including file associations, services, and custom actions, are executed.
MSI files are the preferred installer file format when it comes to application package distribution in enterprise environments. This is due to their standardization and best practices component structure.
All MSI packages support the same installation command lines. To get the full list of all supported MSI command lines, open a cmd, and type msiexec /?.
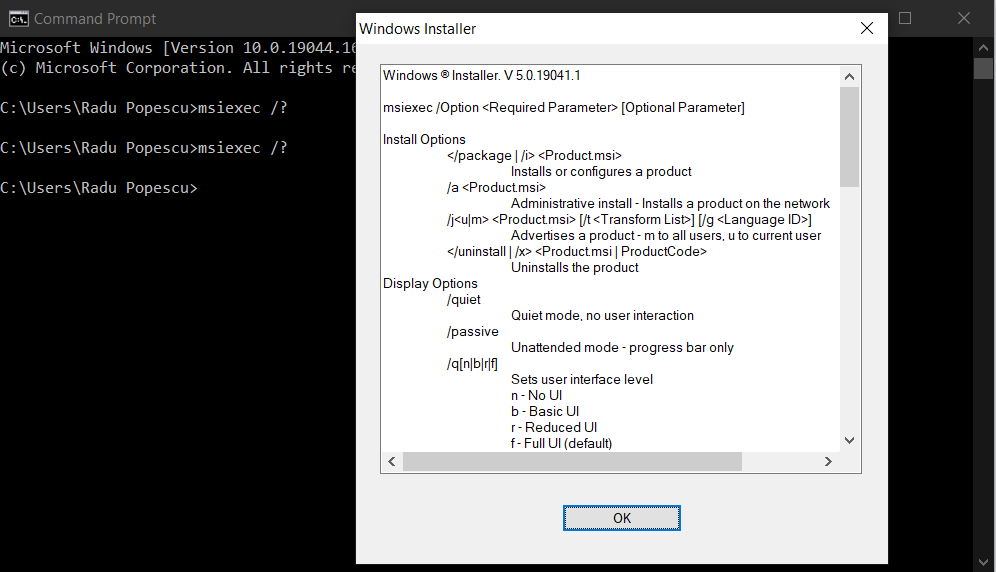
Then, you can apply these options to your setup based on your particular scenario:
- /i to install the package
- /p to patch or update
- /r to repair the package
- /x to uninstall the package
Find more information on support parameters in our Msiexec.exe Command Line article.
How to open and edit an .MSI file?

To see the content of an MSI file format, you can use a 7zip to extract the .msi. By doing this, you will only be able to see the files but not edit them.
Orca

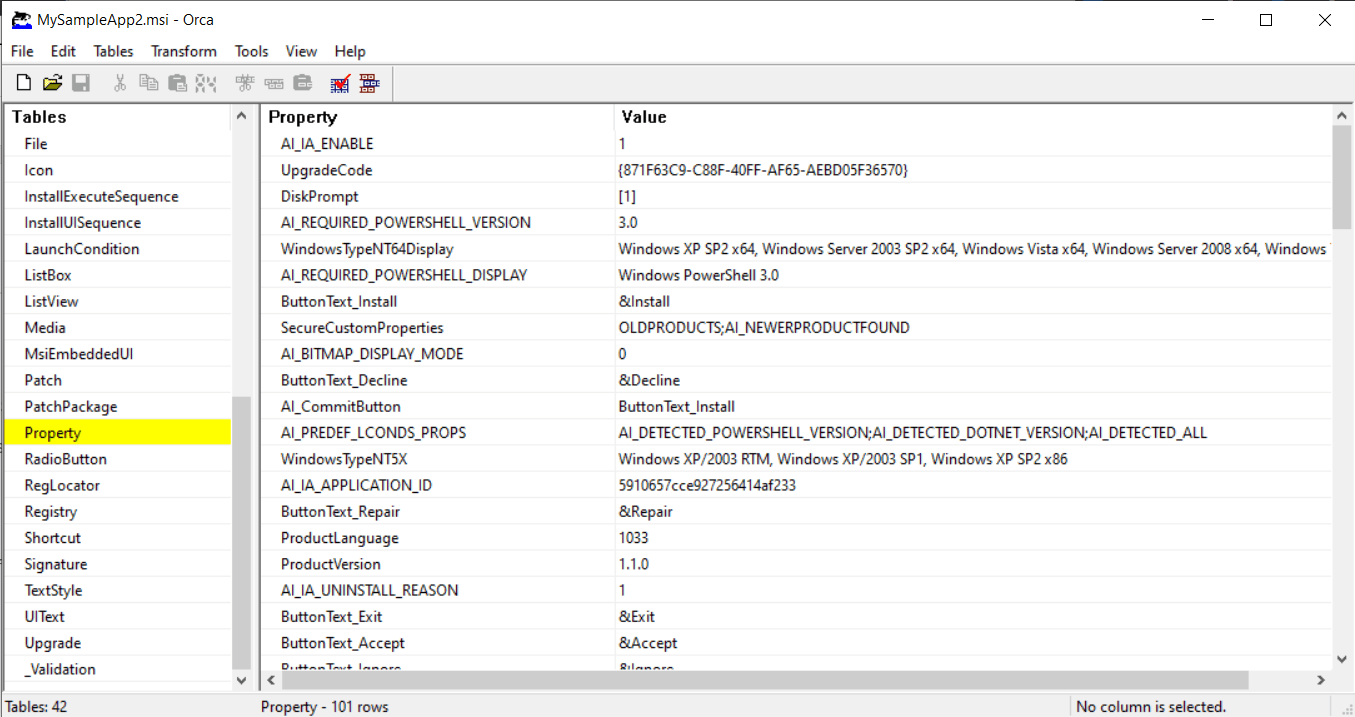
If you are looking into opening and quickly editing an MSI file, you can use the Orca tool. Orca is a free tool that opens the content of the MSI in a table view mode.
Orca comes in handy when you want to get a quick view of the package information and internal structure without actually installing the package. By going to Property table, you can quickly view:
- product name,
- product version,
- manufacturer,
- product code.
Advanced Installer

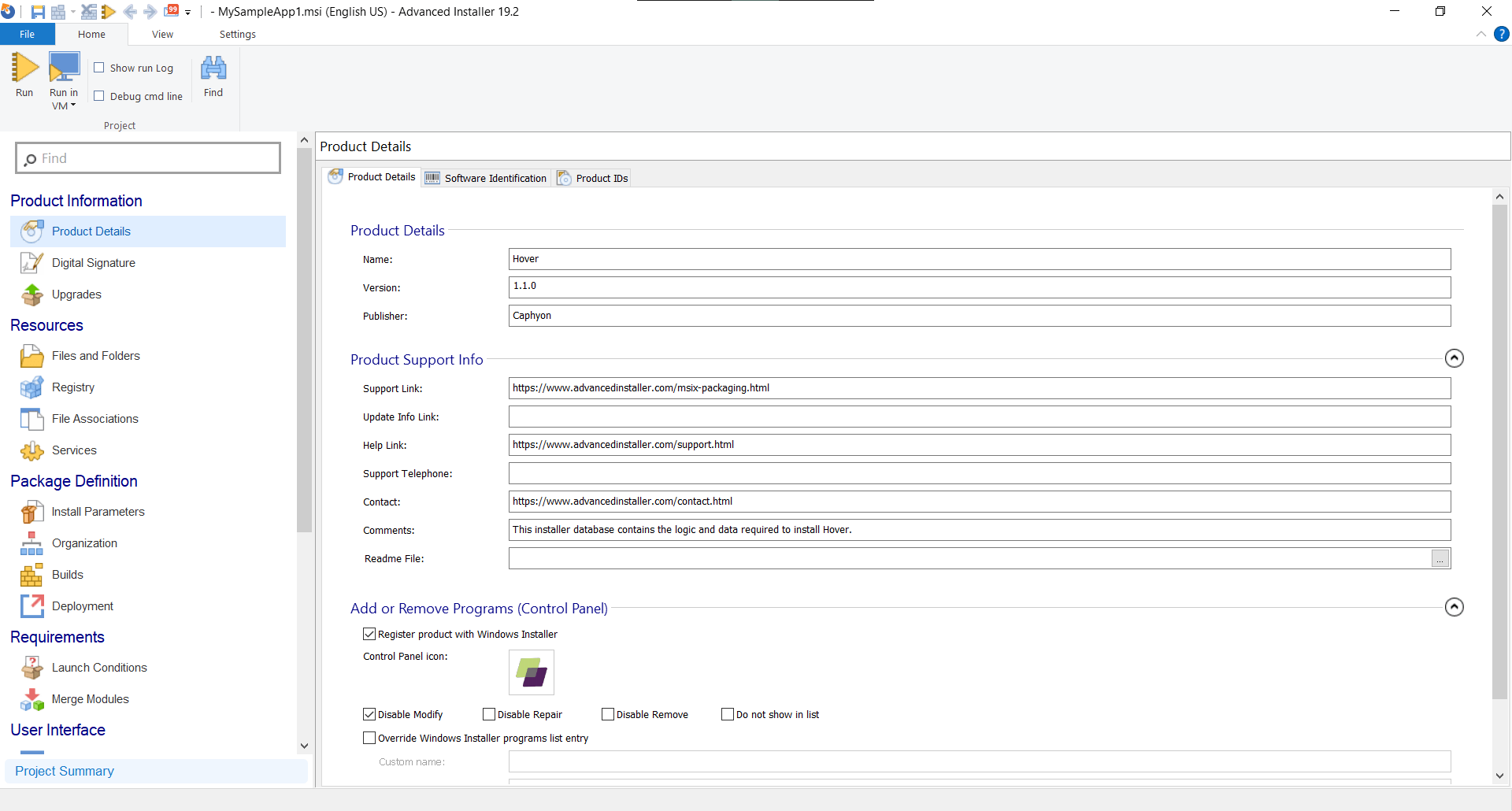
Advanced Installer offers the possibility to open and edit an MSI file easily and intuitively.
Thanks to its rich GUI, you can have a better look over:
- File structure,
- Registry,
- Shortcuts,
- Features,
- Components,
- Services, and more.
Regardless of the tool you choose, you should follow the best practice of using an MST file (transform file) to edit an MSI. This file stores the modifications you want to apply to the MSI package, and it is called during the installation via the TRANSFORMS property.
Msiexec /i msipackagename.msi TRANSFORMS=transformname
Learn more about how to open and edit an MSI in our How to Edit an MSI File using ORCA (plus alternative tool) blog article.
What are the differences between MSI and EXE installers?

Now that we know more about MSI, let us go into how it compares to EXE. What makes these installers different from each other?
Both installers do the same thing: install the software on a computer.
The difference is that EXE files do NOT come only in an installer format. They can be executables of different programs. All Windows applications that you start are executable files.
Due to this characteristic, .exe files could hide malware, which is why MSI files are preferred over the EXE file installers, especially in enterprise environments where security is crucial. Because instead of executing an installation wizard, there is a risk that an .exe file could initiate a malware sequence on the computer.
Still, .exe installers are accepted if they are from a verified source, such as official vendors and not third-party application hosting services.
Another difference between MSI and EXE installer files is the support for install parameters. In the case of the MSI’s, no matter the application, the parameters are the same, but in the case of EXEs, it depends on what tools were used to create the installer and what decisions the developers took while creating it.
We have a dedicated MSI vs EXE installer blog article where we treat the differences between the two setup options extensively.
Are MSI files safe?

While being less popular than the EXE file type, the MSI files are still widely used by Windows users for software installations, and this makes them a target for inserting malware programs and viruses that can endanger your computer security. The recommendation is to have the MSI file scanned with an updated antivirus before running it.
Conclusion

As you can see, MSIs are a reliable installer format that follows best practices and standards. MSIs are especially beneficial in enterprise environments as they could be more secure than their EXE counterparts.
Which type of installer format do you prefer? Let us know in the comments.
FAQ: MSI File - What is, how to open and edit it?
What is an MSI file, and what does MSI stand for?

MSI stands for Microsoft Software Installer. It’s a file format used by the Windows Installer service to install, update, and configure software. MSI files are commonly used by vendors to distribute software in a structured, standardized way.
How is an MSI file different from an EXE installer?

While both MSI and EXE files can install software, MSI is a dedicated installation format that follows a strict set of rules and supports consistent parameters. EXE files, on the other hand, can contain any kind of executable code, including installation logic. This makes EXEs more flexible—but also potentially riskier from a security perspective.
Why are MSI files preferred in enterprise environments?

How do I install or uninstall an MSI file via the command line?
MSI files support standard command-line options via msiexec. For example:
- /i to install
- /x to uninstall
- /f to repair
You can view all options by typing msiexec /? in Command Prompt.
