How to convert a PowerShell Script into an EXE Shortcut
PowerShell is, without a doubt, a powerful and commonly used scripting language for task automation and configuration management. However, sharing these scripts with non-technical users can be challenging, and that’s where converting a PowerShell script into an executable (.exe) file becomes useful.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through why and how to convert PowerShell scripts to EXE.
Why Convert PowerShell to EXE?

There are several advantages to converting .ps1 files into .exe:
- Professional distribution: EXE files look more polished and are easier to execute.
- User-friendliness: you just need to double-click the EXE.
- Code protection: EXEs can obscure your source code better than .ps1.
- Custom icons: You can make your script look more professional by customizing its icon.
- Bypass execution policies: Some users have restricted environments; EXE files can avoid those limitations.
What’s PS2EXE?

PS2EXE takes your PowerShell script and turns it into a standalone .exe file. That means it can run on its own without needing PowerShell open - and it looks more polished, too.
Here’s how it works: the tool wraps your script inside an executable file. When someone runs that .exe, it extracts and runs your original script behind the scenes.
The result? A simple, smooth experience for users, and a reliable solution for developers.
Converting PowerShell script to EXE

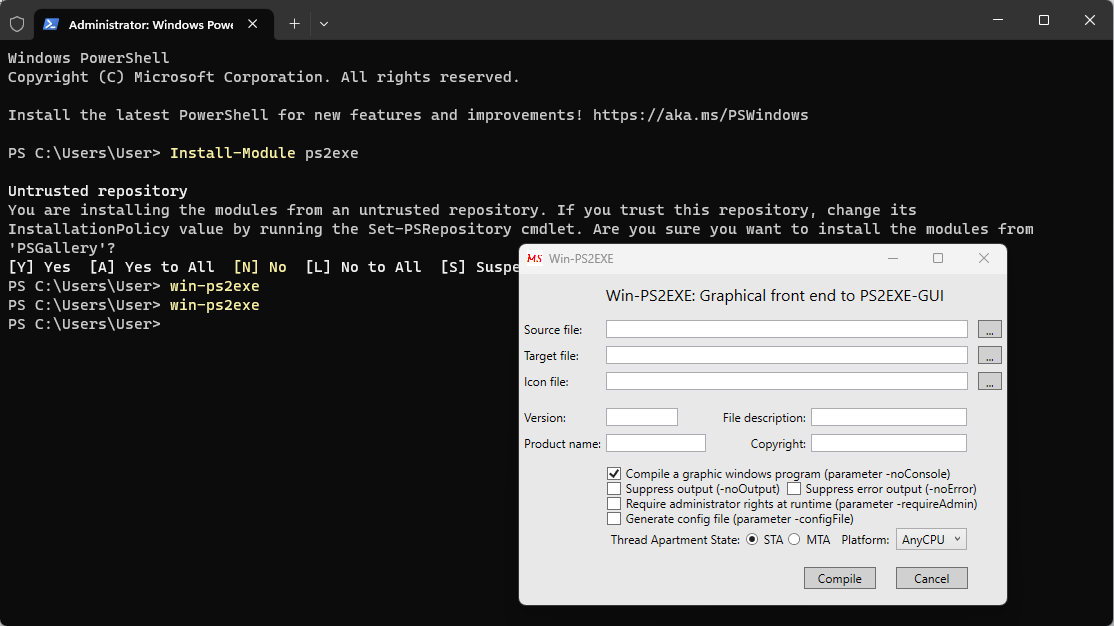
First, you need to get the PS2EXE tool. You can find it online, or you can install it straight away using the following PowerShell cmdlet (run as Administrator):
Install-Module ps2exe
Then, open the GUI with:
win-ps2exe
There, load your script, and hit Compile. Once compiled, you’ll get the corresponding EXE file.
Easy, right? Now, when you run that .exe, it behaves just like your PowerShell script.
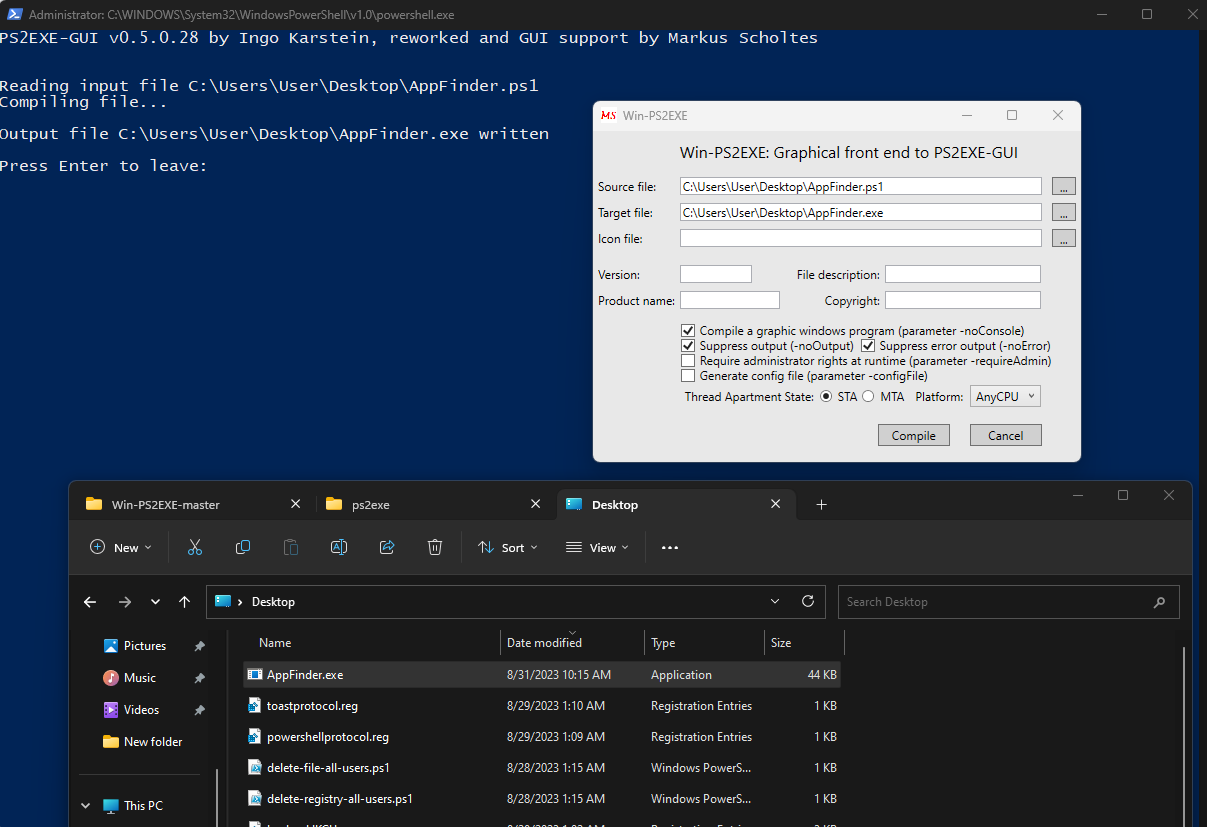
Easy, right? Now, when you run that .exe, it behaves just like your PowerShell script.

Using the EXE in your Package

If your new EXE acts as a launcher for your app, you can easily include it in your package using Advanced Installer.
Here’s how:
1. Open the Files and Folders page.
2. Drag and drop your EXE into the project.
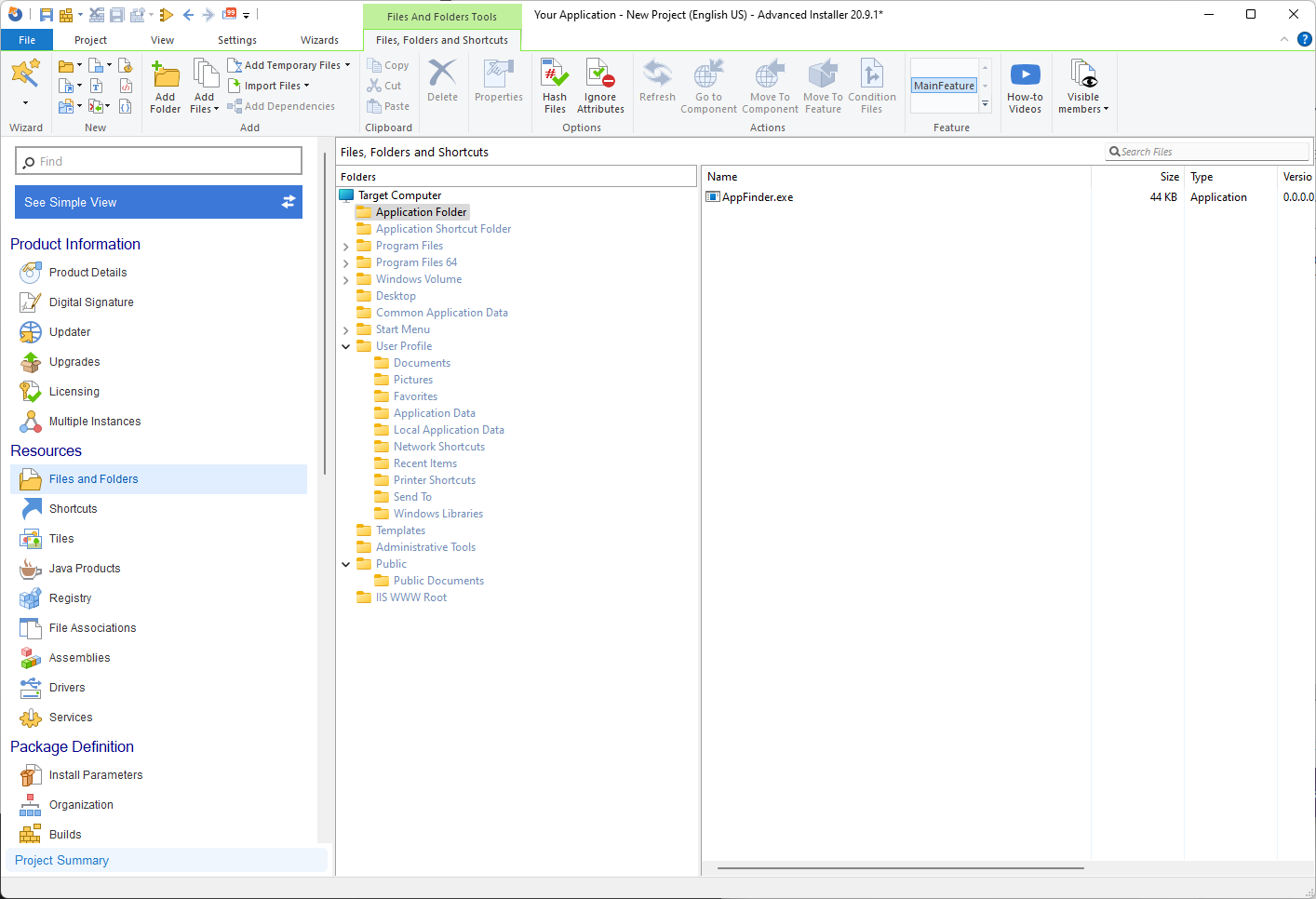
3. Right-click the EXE and choose New Shortcut To > Installed File.
4. Fill in the shortcut details—and that’s it!
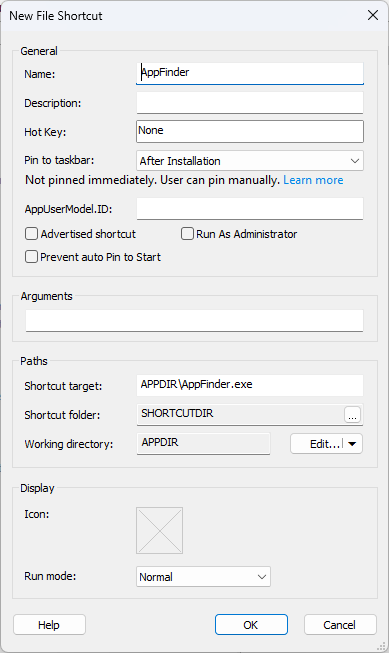
That is how you can easily convert a PowerShell script to an executable and use it in your package.
New to Advanced Installer? Streamline your software packaging with Advanced Installer's 30-day free trial!
Conclusion

Streamlining user experience and ensuring script reliability are essential in software development.
With tools like PS2EXE and Advanced Installer, you can achieve both effortlessly, showcasing the power of effective automation in modern software practices.
Happy converting!
FAQ: How to convert a PowerShell Script into an EXE Shortcut
How to convert PowerShell script to EXE?

To start converting PowerShell script to EXE, get the PS2EXE tool. It's available online in various versions. After refining your PowerShell script, run PS2EXE and input your PowerShell script. It will create the standalone EXE.
How can I install PS2EXE on my system?

To install PS2EXE, open PowerShell with administrative privileges and run the following command: Install-Module ps2exe
This command downloads and installs the PS2EXE module from the PowerShell Gallery.
Can I integrate the generated EXE into an application package?

Yes, the EXE generated from your PowerShell script can be integrated into an application package. This allows you to run specific commands or scripts before launching the main application, helping with the automation and deployment processes.
What are the advantages of converting a PowerShell script to an executable file?

Converting a PowerShell script to an executable offers several benefits that automate your software packaging or deployment experience: Automation: Users can run the script without needing to open PowerShell or have prior knowledge of command-line operations. Deployment: The standalone executable can be easily distributed and run on systems without requiring the PowerShell environment. Professional Presentation: Executables provide a more polished and user-friendly experience, especially when integrating scripts into software packages or deployment processes.
